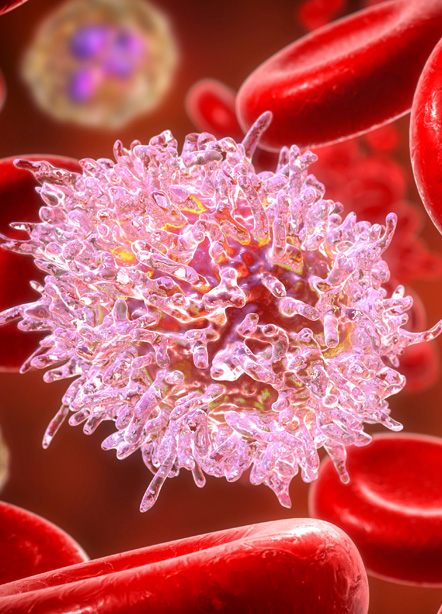
Leukemia is a cancer of the blood, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal blood cells. This uncontrolled growth takes place in your bone marrow, where most of your body’s blood is made. Leukemia cells are usually immature white blood cells. Some types of leukemia are acute, while others are chronic.
Life does not stop when cancer strikes.
We are with you in this fight to win over cancer. We are here to give you the strength to recover through a comprehensive cancer care program.
