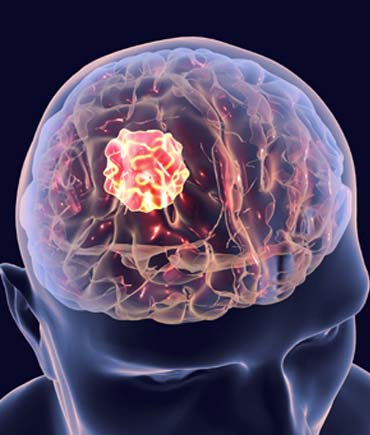
Uncontrolled growth and division of the brain cells or cells of nearby structures such as pituitary gland, nerves, pineal body and brain membranes results in the development of tumors. The tumor may be benign or cancerous. Also, they can be either primary or secondary. While primary brain tumors start in the brain tissues, the secondary ones spread to the brain from other organs, such as the lungs and breasts.
Life does not stop when cancer strikes.
We are with you in this fight to win over cancer. We are here to give you the strength to recover through a comprehensive cancer care program.
