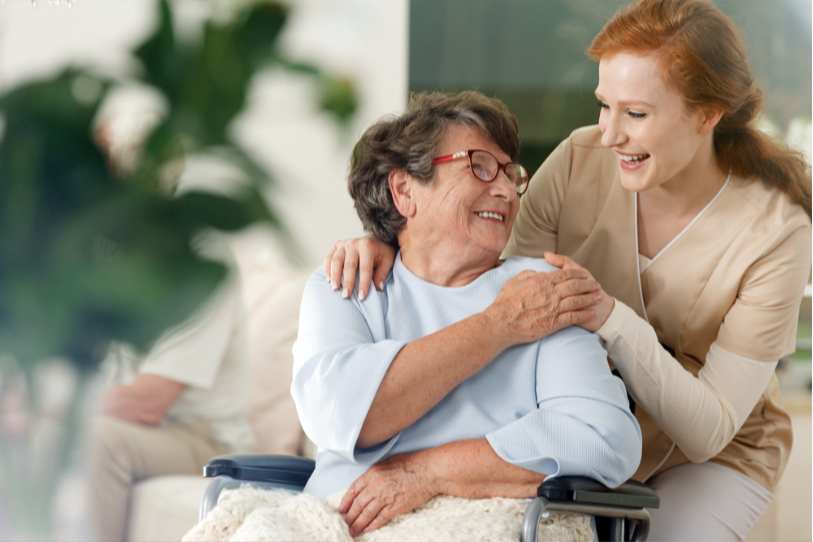
At American Oncology Institute, we offer a continuum of care through your entire journey right from diagnosis, treatment to follow-up care. Through our centres of excellence spread across 11 departments, our team provides a comprehensive range of advanced, multidisciplinary services. Our centres of excellence comprise of the following departments, each collaborate with one another to arrive at a personalized, integrated treatment plan to improve the clinical and emotional outcomes of the disease. A multi-disciplinary team of Medical, Radiation and Surgical Oncologists from AOI together assess the patient’s condition to arrive at the right treatment decisions. There are more than 200 types of cancers. Each cancer needs a customized treatment plan and most of them need more than one type of treatment modality, such as Radiation or Medical or Surgical Oncology. AOI’s experienced cancer specialists create the most effective treatment plan following US University-level guidelines. We are committed to ensure that the best care plan and treatment options are presented to patients to fight the disease and successfully overcome it.
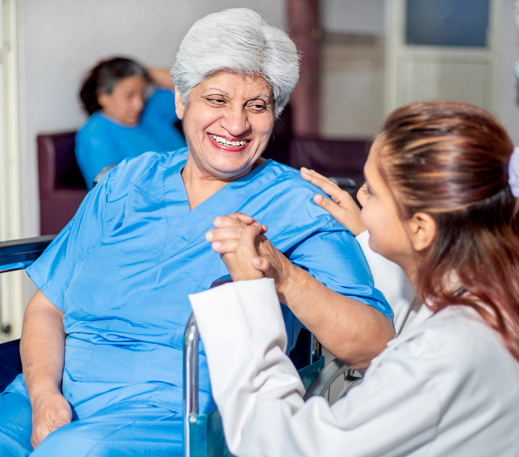

Anaesthesia and critical care play crucial roles in the comprehensive management of cancer patients. Anaesthesiologists evaluate patients before surgery, considering their overall health status, concurrent medical conditions, and potential risks associated with anaesthesia.
Life does not stop when cancer strikes.
We are with you in this fight to win over cancer. We are here to give you the strength to recover through a comprehensive cancer care program.
